Our research shows that a Citizen’s Basic Income would reduce poverty and inequality
Universal basic income has achieved a celebrity status unlike any other idea in the policy field. Here, Dr Malcolm Torry, Director of the Citizen's Basic Income Trust, breaks down the ways it may help inclusive growth.
Our research shows that a Citizen’s Basic Income would reduce poverty and inequality
A recent news item from the All Party Parliamentary Group tells us that new research from the House of Commons library suggests that, if nothing changes, the top 1% of the world’s population could own two-thirds of the planet’s wealth by 2030 if inequality grows at the same rate as it has since the financial crash.
An intuitive response would be to tax wealth or income and to give the money to the poor in the form of means-tested benefits. The problem with that, of course, is that as poorer people earn more, their benefits are withdrawn, and they remain poor. Finding a job, or increasing the number of hours of employment, can often make very little difference to disposable income: so for too many households on Jobseeker’s Allowance, Working Tax Credits, Child Tax Credits, or Universal Credit, it is really difficult to climb out of poverty. Work doesn’t always pay very well.
A counterintuitive and rather different response is to give an unconditional income to every individual. Such an income would not be withdrawn as earnings rose, so it would not suffer from the problem that we have identified with means-tested benefits: but it is counterintuitive as a solution to inequality because to give the same amount to everyone sounds as if it would leave the level of inequality where it is. This is not necessarily the case.
Research at the Institute for Social and Economic Research has shown that an unconditional income for every individual in the UK – a Citizen’s Basic Income – of £63 per week for every working age adult, and different amounts for other age groups, if paid for by reducing to zero the Income Tax Personal Allowance and the National Insurance Contribution Primary Threshold, charging National Insurance Contributions at 12% on all earned income, and raising Income Tax rates by only 3%, would considerably reduce both poverty and inequality
The idea of giving everyone some money is sometimes criticised for being too expensive. Not so. The scheme described here would be revenue neutral: that is, no additional public expenditure would be required.
A frequent difficulty with a revenue neutral tax and benefits reform is that there will always be households that will lose money: and rather too often many of the households that lose money are those on low incomes. One of the virtues of the Citizen’s Basic Income scheme described here is that there would be almost no losses of any significance among low income households.
A further significant result is that although the means-tested benefits structure would be left in place, there would be 7% fewer households on means-tested benefits, 15% fewer households would be on more than £100 per month, and 20% fewer households would be on more than £200 per month. There would be a lot of households more able to escape from means-testing than they are now.
But the results that really matter are that the Citizen’s Basic Income scheme would reduce both poverty and inequality. The detailed results are in the table:
Changes in poverty and inequality indices brought about by the Citizen’s Basic Income scheme
[table id=3 /]
As for the redistribution that would be achieved: it could not be more desirable. There would be substantial proportional increases in disposable incomes for households in the lowest earnings deciles, relatively minor proportional reductions for households in the higher earnings deciles, and significant increases for the ‘squeezed middle’.
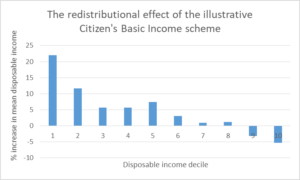
To suggest that inequality could be reduced by giving the same amount of money to everyone might not be intuitive, but if robust microsimulation research of the kind described here shows that giving to everyone an unconditional income could considerably reduce inequality, then it’s a proposal that deserves serious consideration.
Dr. Malcolm Torry, Senior Visiting Fellow, London School of Economics, and Director, Citizen’s Basic Income Trust.
Leave a Reply
Leave a Reply